BECE Past Questions & Answers – 1995 (SCIENCE)
August 1995
SCIENCE
SECTIONB ESSAY
1 hour
[60 marks]
Answerthreequestionsonlyfrom this section.
Illustrate your answers wherever possible, with large, clear andfully labelled diagrams. Creditwill be given for clarity of expression and orderlypresentation ofmaterial.
All questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Explain each of the followingterms: (i) Diffusion
(ii) Surfacetension
(iii) Capillarity
(b) Whydoeswater wetglass?
(c) (i) (ii) Statethe composition of blood
Listthreefunctions of blood
(d)
(i) (ii) (iii)
Describehow ions are formed from atoms
Statetwo differences between aproton and anelectron. Write the chemical symbol for each of thefollowing: (α) an atomofLithium
(β) amolecule ofchlorine
(γ) an atomof oxygen
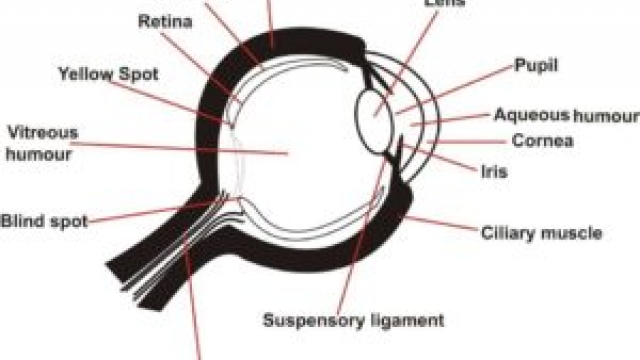
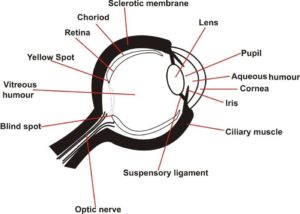
2. (a) Makealabelled diagramofthe human eye.
(b) (i) Name two defects of theeye.
(ii) Statehow each of thedefectsyouhavenamed above can be corrected.
(c) (i) What is a satellite?
(ii) Stateonedifferencebetween anatural andan artificial satellite.
(iii) Statetwo uses of artificial satellites.
(d) Write down thenames ofthe new substances formed when each of the followingsubstances react with dilute hydrochloricacid.
(i) Ammonia
(ii) Sodiumhydroxide
(iii) Calcium carbonate
3. (a) Ineach of theactivities listed below state whetherthe changes that occurarephysical or chemical. Explainyour answers.
(i) An eggis boiled for fiveminutes
(ii) A pieceof bread is chewed in themouth fortwominutes
(iii) A pieceof meat is chewed in themouth fortwo minutes
(iv) A pieceofwood is burntto ashes
(b) Defin eeach of the following
(i) A machine
(ii) Mechanical advantageofamachine
(iii) Velocityratio of amachine
(c) A system of levers is used to overcome aresistanceof 3,000 N when an effort of 150 Nis
applied to it. Calculate themechanical advantageofthe system.
(d) (i) Listthreegeneral causesofdiseases
(ii) State four ways bywhichdiseases canbeprevented.
4. (a) Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction.
(b) Statethe vegetative part that can beused to propagate each of thefollowing plants:
(i) cassava
(ii) onion (iii) banana (iv) yam
(v) ginger
(vi) pineapple
(c) (i) Definedensityofasubstance.
(ii) Describehowyou woulddeterminethe densityofasample ofsoil in the laboratory.
(d) Stateonesolvent foreach of the followingsubstances
(i) Common salt
(ii) Paint (iii) Coal tar (iv) Sucrose
(v) Chlorophyll
CLICK TO VIEW ANSWERS TO PART 2
SCIENCESectionB
SOLUTIONS
ESSAY
1. (a) (i) Diffusion
The random movement of atoms, molecules, orions from one sitein a mediumto
another, resultingin completemixing
Or:
Themovement of particles of asubstance fromaregion ofhigher concentration to a
region of lower concentration
(ii)
SurfaceTension
A condition existingat thesurfaceofaliquid, resemblingastretched elasticskin
Or:
Thepropertyof aliquid that makes its surfacebehavelikeastretched elasticskin
(iii)
Capillarity
The rising and fallingofaliquid’s surfacewhereit is in contact with asolid
(b) Why waterwets glass
The adhesiveforceof attraction between the water molecules and the molecules ofglass is greater than the cohesiveforces of attraction amongthe watermolecules, hencewater tends to clingto theglass orwet theglass.
(c) (i) The compositionof blood
• The red blood cells or corpuscles
• Thewhite blood cells orcorpuscles
• Blood platelets
• Plasma (containing water; dissolved food substances likeglucose, amino acids and fattyacids;hormones, enzymes, metabolic waste substances such as carbon dioxide, salts andurea)
(ii) Functionsof blood
Transports oxygen to thecells of thebody
Transports metabolic waste materials awayfrom the cells of thebody
Transports digested foodnutrients to parts ofthe body
Helps to maintain auniform bodytemperature
Prevents excessiveblood loss byclotting.
Helps to protect thebodyagainstinfections and diseases
(d)
(i)
howions areformed fromatoms
Atoms become chargedwhen theylose orgain electrons in order to bemorestable or
attain a completelyfilledoutershell. When atoms gainelectrons, theybecome negatively
charged ions, knownas anions;when theyloseelectrons, theybecomepositivelycharged
ions, known as cations
(ii)
Difference
(iii) CHEMICALSYMBOL
(α) an atomofLithium Li
(β) (γ) amolecule ofchlorine an atomof oxygen Cl2
O
2. (a) Makea labeled diagramofthehumaneye
(b) (i) Two defects ofthe eye
Longsightedness, short sightedness,
(ii) Longsightedness: Iscorrected usingaconvex(converging) lens
Shortsightedness: Iscorrected usingaconcave (diverging) lens
(c) (i) A satellite
A heavenlybodythat moves round (orbits) alarger heavenlybody
(ii)
Natural Satellite Artificial Satellite
Created byGod(ornature) Manufactured byman
Has no mechanical orelectrical devices Has man-mademechanical or electrical
devices
[anyone]
(iii) Us
es ofartificial satellites
Weatherstudies and forecasting
Telecommunication
SendingandreceivingTV signals
Takingphotographs fromspace for various purposes
Internet networking
Global PositioningSystem (GPS)-aworldwide navigation system
(d) SUBSTANCE FORMED on reaction with diluteHCl
(i) (ii) (iii) Ammonia (NH3)
Sodiumhydroxide (NaOH) Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl)
Sodiumchloride (NaCl)and water(H2O)
Calcium chloride (CaCl2), Carbondioxide (CO2)
and water(H2O)
3. (a) Typeofchangeandexplanation
(i) An egg is boiledforfive minutes
Chemical change, sincethereis a new substanceformed; and the changeisnot reversible
(ii) A pieceof breadis chewedinthemouth for two minutes
Chemical change, sincethereis a new substanceformed; and the changeisnot reversible
(iii) A pieceofmeatis chewedinthemouth for two minutes
Physical change, sinceno new substanceis formed.
(iv) A pieceofwoodisburnt to ashes
Chemical change, sinceanew substanceis formedand the changeisnot reversible
(b) Definitions
(i) Amachine
A mechanical devicethat makes work easierand / or faster
(ii) Mechanical advantageofa machine
The ratio of theload to the effort
Or: = Load / effort
(iii) Velocity ratio ofa machine
The ratio of theeffortdistanceto theload distance
= (effort distance) / (loaddistance)
(c) Mechanical Advantage = Load / Effort
= 3000 N / 150 N
= 20
(NB: themechanical advantagehas no units, sinceitis a ratio)
(d) (i) General causes ofdiseases
Dirtyenvironments
Lack of personal hygiene
Lack of proper nutrition (ordeficiencyof certain food nutrients)
Contact with or sharingitems with person infectedwith communicable diseases.
Lack of regularmedicalcheckups
(ii) Ways ofpreventing diseases
Cleaningourenvironments regularly
Keepingour bodiesandpersonal items cleanalways
Eatingbalanced diets
Avoidingcontact with orsharingitems with persons infected with communicable diseases
Goingfor medicalcheckups regularly
4. (a)
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Occurs bythefusion of two separate sex
cells – male and female
Occurs bythe meiosis of onlyonecell
Results in offspringwithdifferent traits
from parents Results in offspringwithsame traits as
parents
Twoparents of oppositesexareinvolved Onlyoneparent is involved
(b) PLANT VEGETATIVEPART
(i) cassava stem cutting
(ii) onion bulb
(iii) banana sucker
(iv) yam stem tuber
(v) ginger rhizome
(vi) pineapple sucker / crown
(c) (i) Density ofa substance
Themass per unit volume ofthe substance
Or: Density = mass / volume
(ii) Determinationof density ofsoil
– Themass, M, of agivenquantityof thesoil is determined using abeam balanceor chemical balanceor electronicscale
– A measuringcylinder is filled with waterto a suitable volume, V1and the readingis recorded.
– Thesoil is gentlypouredinto the measuring cylinder and the new (higher)volume, V2is read and recorded
– Thevolumeof thesoil is calculatedas V2– V1
– Thedensityof thesoil is calculatedas =
(d)
(i) SUBSTANCE Commonsalt SOLVENT
water
(ii) Paint water (ifemulsion), turpentine (if oil paint)
(iii) Coal tar petrol / kerosene
(iv) Sucrose water
(v) Chlorophyll alcohol






