BECE Past Questions & Answers – 2006 (SCIENCE)
April2006
SECTION B
1 hour15 minutes
ESSAY [75marks]
This section is in two parts, I and II
AnswerQuestion1ofPartIand any other three questions in Part II.
Credit will be given for clarity of expression and orderly presentation of material
PART I
[30 marks]
(Compulsory– Answer all of Question 1)
1. (a) The diagram below shows the electrical method of magnetizing a nail.
Study the diagram and use it to answer the questions that follow.
(i) Give the names of the parts of the circuit labelled I,II and III (ii) List two substances that can be made into a magnet.
(iii) State two other methods of making magnets.
(iv) Name one material that is used in making an electrical wire
(v) Give two properties of the material you named in (iv) which makes it useful as a wire.
[10 marks]
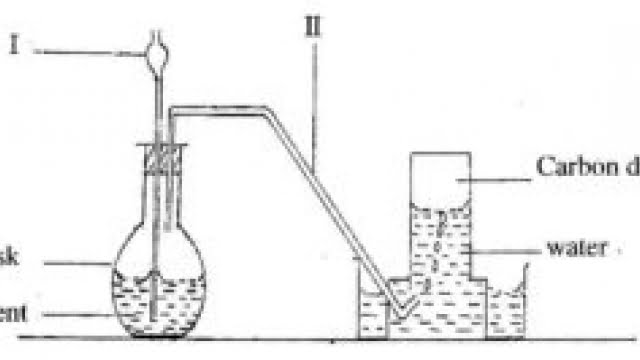
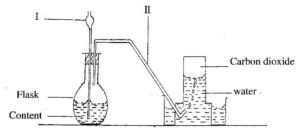
(b) The diagram below shows the set-up for the preparation of carbon dioxide in the laboratory.
(i)
(ii) Name the parts of the set-up labelled I and II
Give the name of the method of gas collection shown in the diagram.
(iii)
(iv) Give one property of gases collected over water
What will happen if component I does not dip into the contents of the flask?
(v)
(vi) List two compounds that form the content of the flask.
Write down the systematic name of carbondioxide. [10 marks]
(c)
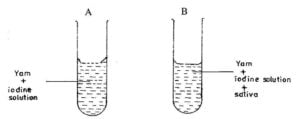
In an experiment,yam pap is put into two test tubes A and B containing iodine solution.
The test tubes are warmed slightly to a temperature of 37°C and saliva is put into test tube B
(i) State the colour of the content of test tube A
(ii) State the colour changes of the contents in test tube B after about 3 minutes.
(iii) Fehling’s solution is added to the contents of test tube B after the3 minutes and it turns brick- red. What food substance is present?
(iv) Give two functions of saliva in eating.
(v) Why was it necessary to warm the contents of the test tubes to about 37°C?
(vi) Give two aims of the experiment. [10 marks]
PART II
[45 marks]
(Answer three questions only from this part)
2.
(a)
(i)
State two conditions that are required for photosynthesis to take place.
(ii) How would you show that starch is formed during photosynthesis?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation to show the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen.
(c) (i) What is a satellite?
(ii)
Give one example of a natural satellite.
(iii)
List two uses of artificial satellites.
3. (a) Define
(i) self-pollination
(ii) cross-pollination
(b)
State two ways in which cross-pollinated plants are better than self-pollinated plants.
(c)
Sodium chloride is prepared by the reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.
(i) Write a balanced equation for the reaction
(ii) What is the name given to this reaction?
(d)
Describe an experiment to show that pressure acts in all directions in a liquid
4. (a) (i) What is a vector of a disease
(ii) State two methods each by which the vectors of the following diseases can be destroyed:
α) river blindness;
β) malaria
(b) Write down the systematic names of the following compounds:
(i) (ii) CaCO3
FeS
(iii) (iv) NaCl
NaOH
(c)
(i)
Give the two properties that are common to all states of matter.
(ii)
In an experiment to determine density, a stone of mass 60 g is put into a bowl containing water
If the level of the water rises from the60 cm3mark to 75 cm3, determine the density of the stone.
5. (a)
(b) Mention five differences between plants and animals
Define each of the following terms,giving one example in each case
(i) (ii) compound element
(c)
(i)
Give two differences between an electrical insulator and a conductor.
(ii)
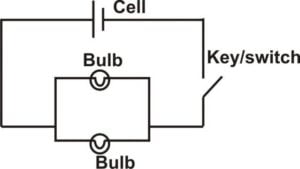
Draw and label a simple electrical circuit made up of a cell and a switch connected to two electrical bulbs connected in parallel
CLICK TO VIEW ANSWERS TO PART 2
SCIENCE Section B
SOLUTIONS
ESSAY
1. (a) (i) I – Cell
II – Key or switch
III – Solenoid or coil
(ii) Substances: Iron (Fe), Steel, Nickel (Ni), Cobalt(Co) [any two]
(iii) Methods of making magnets
• Single stroking
• Double stroking
• Induction
• Hammering [any two]
(iv) Material for electrical wire:
Copper (Cu), aluminum (Al), steel, iron (Fe),gold(Au), silver (Ag), and platinum (Pt) [anyone]
(v) Property of material
ductile,
malleable,
low resistivity
high tensile strength [any two]
(b) (i) I – thistle funnel
II – delivery tube
(ii) Upward delivery or down ward displacement of water
(iii) They are
• insoluble in water;
• less dense than water [anyone]
(iv) The gas produced will escape through the thistle funnel
(v) Content of flask
• Calcium carbonate [CaCO3] – (reactant)
• Hydrochloric acid [HCl] – (reactant)
•
• Calcium chloride
Water [CaCl2] [H2O] – (product)
– (product)
(vi) Carbon(IV) oxide
(c) (i) Blue black
(ii)
pale blue black
(iii)
maltose or reducing sugar
(iv)
Functions of saliva
makes the food softer for easier chewing and swallowing
Contains the enzyme ptyalin, which breaks down carbohydrates to reducing sugar
(v) To attain thenormal bodytemperature, at which the enzyme in salivacanwork efficiently
(vi) Aims ofexperiment
To show that saliva contains enzymes that digest carbohydratesorstarch
To show that digestion ofcarbohydrates starts in themouth, wheresalivais produced
To show thatyamcontains starch
2. (a) (i) Thepresenceof water, carbondioxide, chlorophylland light
(ii)
Experiment
Pluck aleaf from aliving plantthat has been in sunlight for3 ormorehours.
Boilthe leaf to kill the cells andstop the process of photosynthesis
Placethe leaf in warmalcohol forsomeminutes to remove the chlorophyll
Placethe leaf in warm waterto washawaythealcohol and softenthe leaf
Placeafew drops of iodinesolution on the leaf
Observation andConclusion
It is observed that the leaf turns blue-black. Thiscolouration indicates thepresenceof starch. This show that starch is formed duringphotosynthesis
(b) H2 + O2 → 2H2O
(c)
(i) (ii)
A satellite is anyheavenlybodythat orbits (revolves around)alarger one. Themoon is a natural satelliteof the earth;
Theplanets arenatural satellites ofthe sun
(iii) Us
es ofartificial satellites
Weatherstudies and forecasting
Telecommunication
SendingandreceivingTV signals
Takingphotographs fromspace for various purposes
Internet networking
Global PositioningSystem (GPS)-aworldwide navigation system
3. (a) (i) Self-pollinationis
Thetransfer ofpollengrains from an antherof aflower to thestigmaof thesame flower
(ii) Cross-pollinationis
Thetransfer ofpollengrains from the antherofa flower to thestigmaof another flower on anotherplant ofthe samekind
(b) Produceoffspringthat aremoreresistant to diseases
Produceoffspringthat arestronger andhealthierthan parents
Causes geneticvariations in offspringthat makethem betterthen parents [anytwo]
(c) (i) HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
(ii)
Neutralization reaction
(d) Experiment
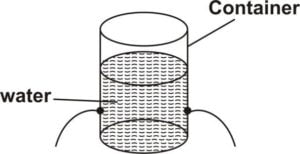
Get a suitable container and makeholes of equal sizes at thesameheight around it(as shown in thediagram above
Pour water (or other liquid)into the container to fillit
Thewater (orliquid) comes out through the holes in alldirections and with thesamepressure
This shows that pressureacts in alldirections in aliquid
4. (a) (i) A vectoris
an agent that carriesandspreads organisms that cause diseasefrom infected organisms to non-infected ones.
(α) riverblindness
Killingthe vector, theblack fly, byspraying chemicals onto the riverbanks or wherever theyarelocated
Destroyingthebreeding grounds of theblackflybyclearingthe bushes alongthe banks of riverswheretheyarefound.
(β) malaria
Killingthe mosquito byspraying appropriate insecticide at places wheretheyare located
Killingthe mosquitoes byspraying room with insecticide.
Destroyingthebreeding grounds of mosquitoes byclearingchokedgutters
Destroyingthehidingplaces of mosquitoes byclearingbushes
Killingthe larvaeof mosquitoes bypouringoilonthe surfaceof stagnant water
Killingmosquitoes byusinginsecticide treated mosquito nets
Killingmosquito larvaein ponds bystockingwithfish that feed on the larvae.
(b) (i) Calcium trioxocarbonate (IV)
(ii)
Iron (II)sulphide
(iii)
SodiumChloride
(iv)
Sodiumhydroxide
(c) (i) Properties
Matter has mass
Matter has volume (occupyspace)
(d) Density = mass ÷ volume
Mass ofstone = 60kg
Volume ofstone
= 75cm3– 60cm3
= 15cm3
Density
= 60 g÷15 cm3
= 4 g/cm3
or 4 gcm-3
5.
(a) Differences
PLANTS ANIMALS
Manufacturetheirownfood (photosynthesis) Do not manufacturetheirown food
Cannot move freelyfromplaceto place Ableto move freelyfromplaceto place
Mostplants do not respond quicklyto stimuli Respond quicklyto stimuli
Haveacellwall Do not haveacellwall
Have chloroplasts, whichcontain chlorophyll Do not have chloroplast
Excess carbohydratesarestored as starch Excess carbohydrates arestored asglycogen
Absorb carbondioxide forphotosynthesis and
releaseoxygen aswasteproduct Inhale oxygenforrespiration and release carbon
dioxide as waste product
Cells havelargeand permanent vacuoles Cells havesmall temporaryvacuoles
Growth takes place at specific parts Growth takes place atallparts
[any five]
(b) (i) A compound is a substance formed bythe chemical combination of two ormore elements in definite proportions
Example, HCl, orNacl, orCa(OH)2, or CaCl2, or NH3,orMgCO3, etc
(ii) An element is a substancethat is madeup ofonlyonekind of atoms.
Example are: Calcium, or Sodium, orMagnesium, or Argon, or Sulphur, etc
(c) (i)
ElectricalInsulator Electrical Conductor
Does not conduct electricity Conducts electricity
There arenofree electrons to conduct
electricity There are free electronswhich make
electrical conduction possible
Narrowconduction energyband Wide conduction energyband
Wide forbidden gap between valence
and conduction band No forbiddengap between valenceand
conduction band
(ii) simple electrical circuit