BECE Past Questions & Answers – 2008 (SCIENCE)
April2008
SCIENCE2
1¼hours
ESSAY
[75marks]
This paper is in two sections, A and B
AnswerQuestion1in Section A and any other three questions in Section B. Credit will be given for clarity of expression and orderly presentation of material
SECTION A
[30 marks]
(Compulsory– Answer all of Question 1)
1. (a)
In an experiment, as in the set-up above, two glass containers A and B of different sizes are joined together with a tube and clipped.
Water is poured into container A to a height of 30cm and are d liquid is poured into B to a height of
10 cm. The clip is then removed so that the liquids join together.
(i) State two observations that will be made immediately the clip is removed. (ii) Explain the observations in (i)
(iii) What two observations will be made after along time?Explain.
(b) The set-up below is used in the preparation of ammonia gas in the laboratory.
Study it and answer the questions that follow
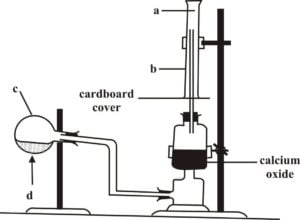
(i) Name the parts labeled a,band c.
(ii) What is the meaning of the arrow sign d? (iii) What is the function of the calcium oxide? (iv) Why has c been tilted downwards?
(v) State the method by which the gas is collected. (vi) How will you test for the gas?
(vii) Give the names and the chemical formulae of the compounds that form the content of c.
(c) In an experiment, a leaf that is partly green and partly yellow is plucked from a tree and the leaf is
I. boiled for a minute
II. dipped in warm alcohol
III. washed in cold water
IV. dipped in iodine solution
One part of the leaf turns blue-black after the dipping in iodine solution while the other part remains unchanged.
(i) Explain why each of the processes I, II and III is carried out. (ii) Which part of the leaf turns blue-black?Explain.
(iii) Why does the other part of the leaf not change colour? (iv) What conclusion can you draw from the experiment?
SECTION B
[45 marks]
Answer any three questions from this section
2.
(a)
(i) (ii)
State the difference between an opaque object and a translucent object. Give one example each of an opaque and a translucent material.
(b)
(i) (ii)
What is the importance of seed dispersal?
Name two types of fruits and state their mode of dispersal.
(c)
(i) (ii) (iii)
What is recycling?
Give two advantages of recycling of materials
List three recycled products in Ghana.
3. (a) (i) Explain the term bed wetting?
(ii) State two diseases that may result from bed wetting
(b)
(i) (ii)
State the difference between hard water and impure water.
Give the stages involved in the treatment of water for a community.
(c) A piece of stone has a mass of 36.0g. When it is put into water in a glass container, the level of water rises from 60.0 cm3to 90.0 cm3.
(i) Calculate the density of the stone.
(ii) Explain what will be observed when the stone is put into another liquid of density1.4 gcm3?
4. (a) (i) (ii) What is an echo?
State two uses of echoes
(b)
(i) (ii)
State three diseases that affect the respiratory system of human.
Name one method each by which the diseases you have named can be prevented.
(c)
(i) (ii)
What is biotechnology?
List three products that are obtained from biotechnology.
5.
(a)
(i) (ii)
Define pressure
State three applications of pressure in everyday life.
(b) State four functions of the liver in digestion
(c) (i) What is a compound?
(ii) Give two properties of a compound
(iii) Write down the name and the chemical formula of the compound formed between the
following elements:
(α) hydrogen and chlorine
(β) magnesium and oxygen
CLICK TO VIEW ANSWERS TO PART 2
SCIENCE2
SOLUTIONS
ESSAY
1. (a) (i) The height of the red liquid will increase as the height of the water reduces
The red liquid mixes with the water as its particles move into the water
(ii) Since the water is higher,it has greater pressure. Therefore it moves in the direction of the lower pressure
Diffusion occurs as the molecules of the red liquid move from a region of higher concentration to the water region, which is of lower concentration
(iii) A liquid uniform mixture, which has the same colour and concentration, will be formed
Since the mixture is essentially uniform, but the containers are of different sizes, the level of liquid in the smaller diameter container,B, will be slightly higher than the level in container A, due the principle of capillarity.
(b) (i) a – ammonia gas b – gas jar
c – round bottomed flask
(ii) d – Heat
(iii) The calcium oxide removes the moisture or water content from the gas produced (iv) c is tilted downwards so that condensed water does not get back into the hot flask (v) Upward delivery(or downward displacement of air)
(vi) Gas has pungent smell
Or: Moist red litmus paper turns blue in the presence of the gas
Or: The gas produces fumes in the presence of concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl)
(vii) Any alkali plus ammonium chloride,
eg, NaOH andNH4Cl or KOH and NH4Cl or
Ca(OH)2and NH4Cl or Mg(OH)2and NH4Cl
(c) (i) I The leaf is boiled to stop the process of photosynthesis by killing the cells
II.
The leaf is dipped in warm alcohol to remove the chlorophyll(the green matter)
III
The leaf is washed in cold water to wash away the alcohol and soften it.
(ii) The part that was green
The blue-black colouration indicates the presence of starch, which means that photosynthesis occurred at the green part to produce starch.
(iii) It does not contain starch. This implies that photosynthesis did not occur there due to the absence of chlorophyll,which is necessary to absorb light for photosynthesis.
(iv) Chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis to occur.
2. (a) (i) An opaque object does not allow light to pass through, whereas
A translucent object allows some amount of light to pass through diffusely.
(ii)
Opaque -wooden or metallic materials,mirror, the earth,mammals, etc
Translucent -fabric, lightly-coloured water, oily spot on paper, frosted glass, etc
(b) (i) Importance of seed dispersal
Enables plants to grow in other areas;
Prevents the over-crowding of plants in one area
Helps to reduce the rapid spread of plant diseases
Prevents competition for soil nutrients among plants
(ii) FRUIT MODE OF DISPERSAL
Tridax, silk cotton,
– Wind
Cowpea, Crotalaria, Balsam
– Explosive Mechanism
Coconut,
– Water
Orange,Guava,Tomatoes, Maize – Animals (man and others)
(c) (i) Recycling – The process of converting waste materials into new useful products
(ii) Advantages of recycling
Employment /income generation for people
Pollution of the environment by waste materials is reduced
Reduction of resources for production
Saving of money that would have been used for controlling waste
Generation of energy for increased production [any two] (iii) Recycled products in Ghana
Paper, biogas, polythene materials, rubber, particle boards, iron rods,etc [any three]
3. (a) (i) Bed wetting – The involuntary passage of urine usually during sleep.
(ii) Bed wetting diseases- ringworm, skin rash, eczema, etc [any two]
(b) (i) Hard water is water that does not easily lather with soap
Impure water is water that contains certain substances that make it unwholesome for drinking.
(ii) Stages for water treatment
Letting water run through filters to remove suspended materials
Adding alumto cause sediments to settle
Adding chlorine to kill germs
Exposing water to air(aeration) to remove any bad smell
(c) (i) Density = mass ÷volume
Mass of stone= 36.0g
Volume of stone
= 90.0cm3– 60.0cm3
= 30.0cm3
Therefore Density of stone = 36.0g÷30cm3
= 1.2 g/cm3
(ii) Since the density of the stone (1.2g/ cm3) is less than the density of the other liquid
(1.4g/cm3), the stone will float on the liquid
4. (a) (i) An echo is the result of the reflection of sound when it strikes a hard surface.
Or: the repetition of a sound caused by the reflection of sound waves from a surface
(ii) Uses of echo
Determination of distances by bats
Determination of velocity of sound
Clinical diagnosis in ultra-sound equipment
Mineral exploration
Determination of sea bed depth in special equipment
Detection of possible obstacles by ships [any two]
(b) (i) Common cold, Tuberculosis, Whooping cough, Pneumonia, Asthma,Lung cancer
(ii) Common cold: avoid over-exposure to cold air or dusty environment
Tuberculosis:
Avoid sharing cutlery, cups and glasses with infected persons
Whooping cough:
get vaccinated
Pneumonia:
wear warm clothes or avoid exposure to cold conditions
Asthma:
keep away from dust, pollen grains, smoke or other substances that one is allergic to
Lung Cancer:
avoid smoking
(c) (i) Biotechnology: The practical use of biological processes for man’s benefit
(ii) Products obtained from Biotechnology
Cheese,yoghurt, butter,bread, wine, beer, vaccines, insulin, antibiotic drugs, food supplements, biogas, etc [any three]
5. (a) (i) Pressure is the force per unit area
Or Pressure = force/area
(ii) Applications of pressure in everyday life
Pumping a car tyre;
opening a sealed can with a pointed knife;
pumping liquid from a low level to a higher level;
Drawing a drink into the mouth with a straw;
drawing liquid using a syringe [any three] (b) Functions of the liver in digestion
Converting glycogen to glucose for use by the body
Producing bile, which is used to emulsify fats
Storing excess glucose as glycogen or starch
Removing excess glucose from blood
(c) (i) Compound: a substance formed by the chemical combination of elements in fixed proportions
Or: a substance containing two or more elements that are chemically combined
(ii) Properties of compounds
Their properties are different from the individual constituents that form them.
Heat changes occur when they are being formed
Their constituents are in a fixed ratio
Compounds cannot be broken down to obtain their reactants by any known physical means
(iii) (α) Hydrogen+ chlorine
→ hydrochloric acid (HCl)
(β) Magnesium+ oxygen
→ magnesiu





